Lightning arrester of photovoltaic power plants
Lightning Arrester for Photovoltaic Power Plants as Lightning Protection
During my practice as a Service Technician and Inspection Technician of electrical installations and lightning conductors, I often encounter a case of a poorly built or poorly made lightning conductor. The explanation for this phenomenon is simple - the investor who receives the project often does not understand what the individual devices consist of. In the European Union, the standard EN62 305 - 1 to 4 (in Slovakia it is STN EN 62 305) is valid as lightning protection, the contents of which are the basic requirements for the design of lightning protection. In it you can find a lot of theoretical information on how lightning protection should be properly designed. In this article, however, I would like to give a more practical view of protection, also for the general public.
I will discuss some basic breakdowns of the system used and how to best protect your equipment.
Passive lightning arrestor
Passive lightning arresters are most often found on buildings in two versions, let's try to break down both of them.
In order for this lightning arrester to sufficiently protect the equipment, it is necessary that the collectors (collector bars) overhang the equipment as much as possible so that in the event of a lightning strike, it is these collectors that will catch the lightning in the event of a lightning strike.
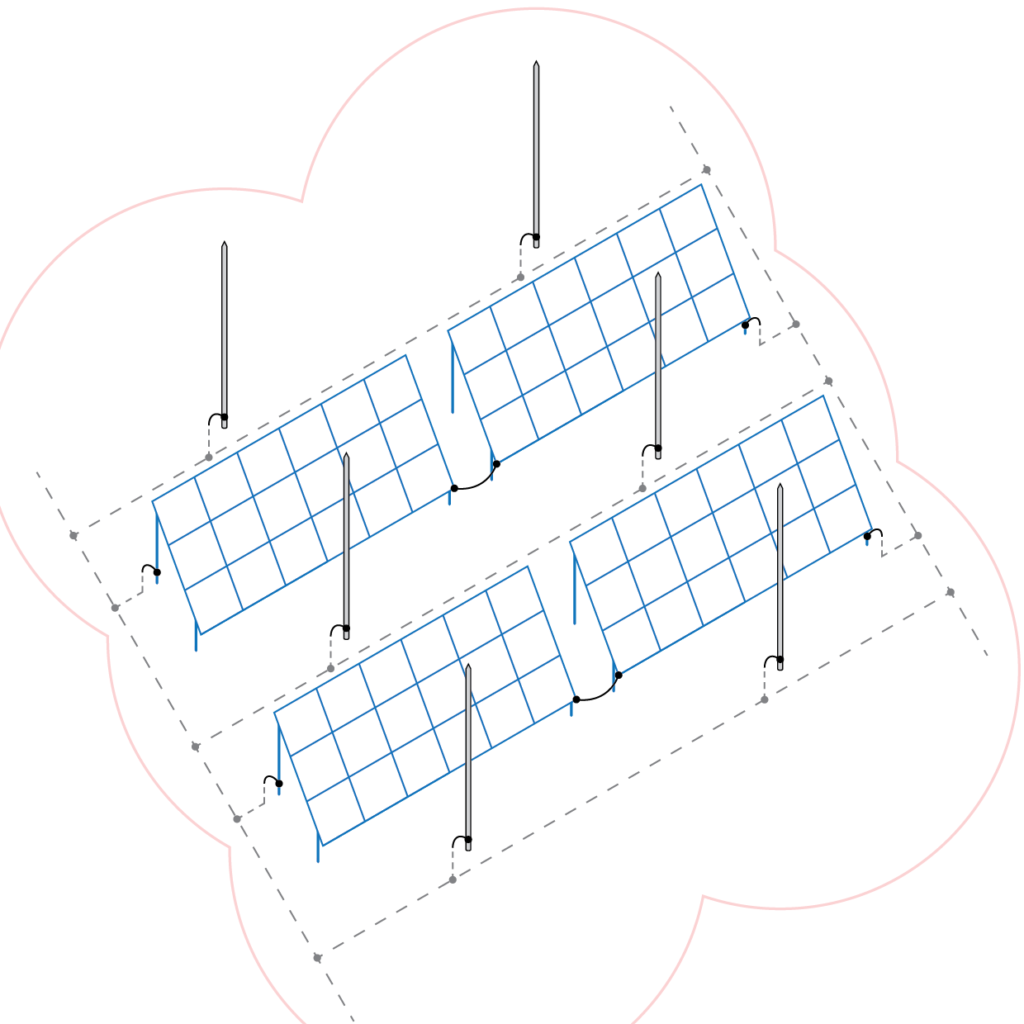
Figure 1
At Figure 1 it is possible to see the basic layout of the lightning busbars connected to the common earthing system.
Advantages:
- everything is connected to one potential
- the same earth resistance at all locations
Disadvantages:
- during the strike we can bring "lightning" directly to the inverters and other important equipment
- the possibility of damage to surge protectors, which are costly
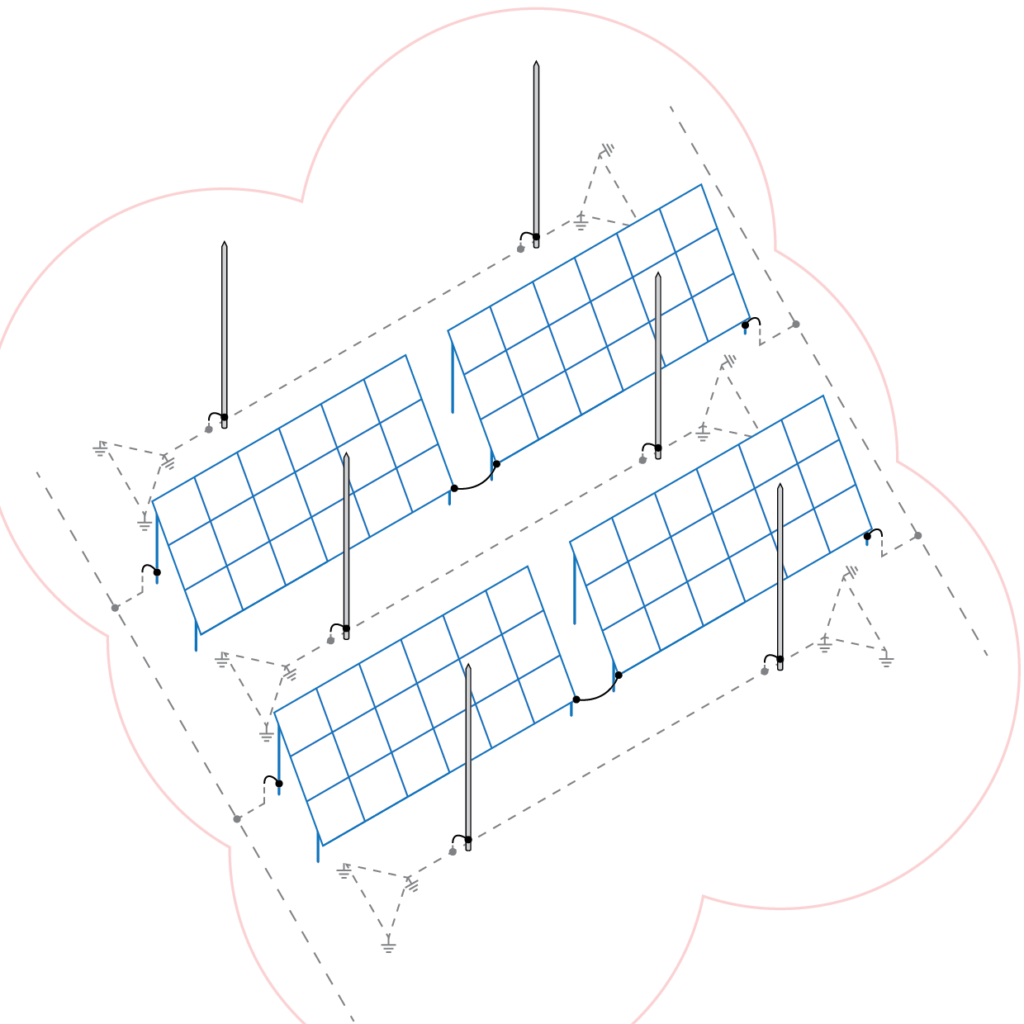
Figure 2
Figure 2 shows a passive lightning arrester with a separate earthing system (remote LPS).
Advantages:
- unwanted lightning current is not conducted to other devices when lightning strikes
Disadvantages:
- Slightly more investment-intensive solution, due to the construction of isolated downpipes
active lightning arrester
This type of lightning arrester is only used in some countries. Its advantage is that it can protect a much larger area than a passive lightning protection system, therefore the number of lightning rods is smaller and even with the relatively high purchase price of the head, the whole design is less expensive.
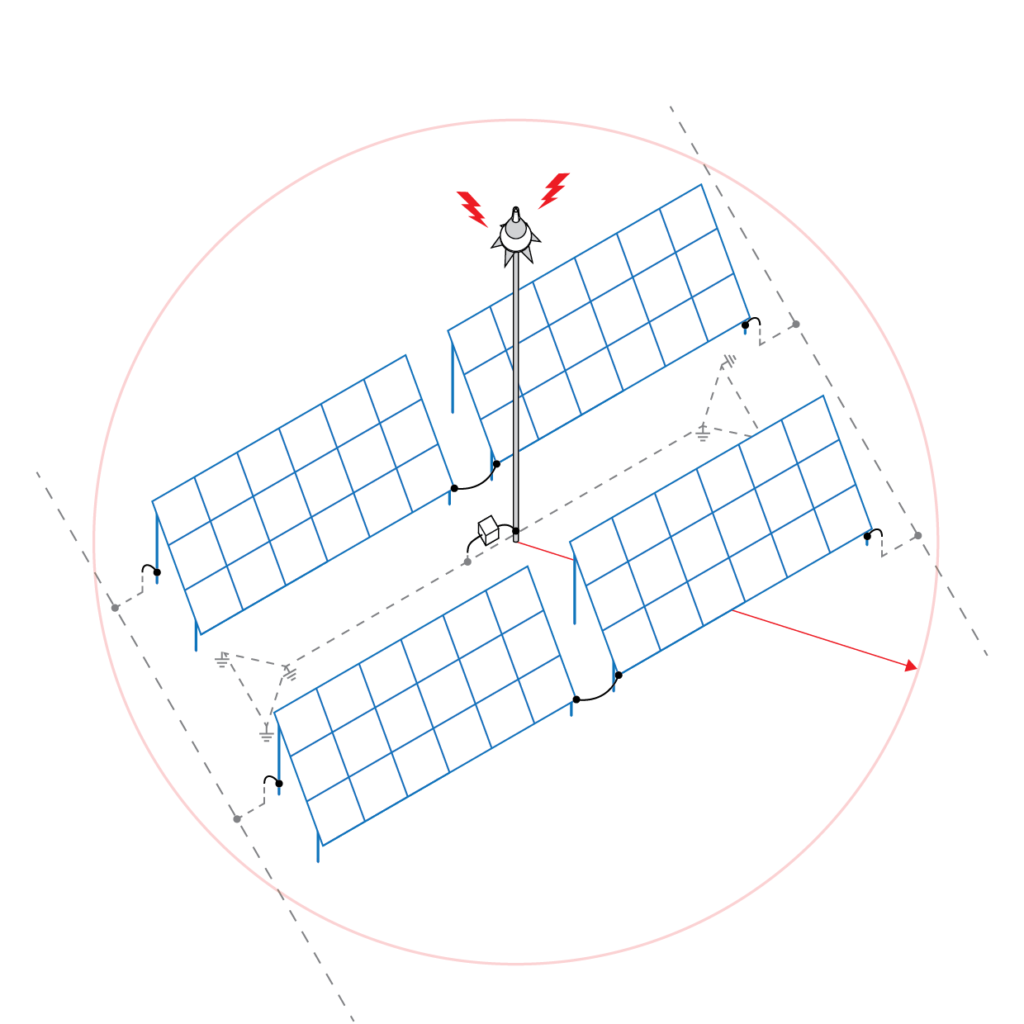
Figure 3
Figure 3 shows an active lightning arrester with a separate earthing system (remote LPS).
Advantages:
- unwanted lightning current is not conducted to other devices when lightning strikes
- not as much material is needed, which can make it cheaper than classic LPS
Disadvantages:
- more frequent inspection with special measuring equipment
- the design must be of higher quality with more extensive knowledge of their functionality.
- a long-standing expert debate on their actual effectiveness.
Each lightning arrester must be regularly inspected and measured over a period of 2 to 5 years, all depending on the technology used and the local climatic conditions. It is important that the lightning arrester is correctly constructed and has a sufficiently low earth resistance, up to a maximum of 10Ω, during the whole period. It is necessary that the person carrying out the inspection of the installation has sufficient knowledge and experience in the field of lightning protection.
Pictures of the PV damage after the storm:
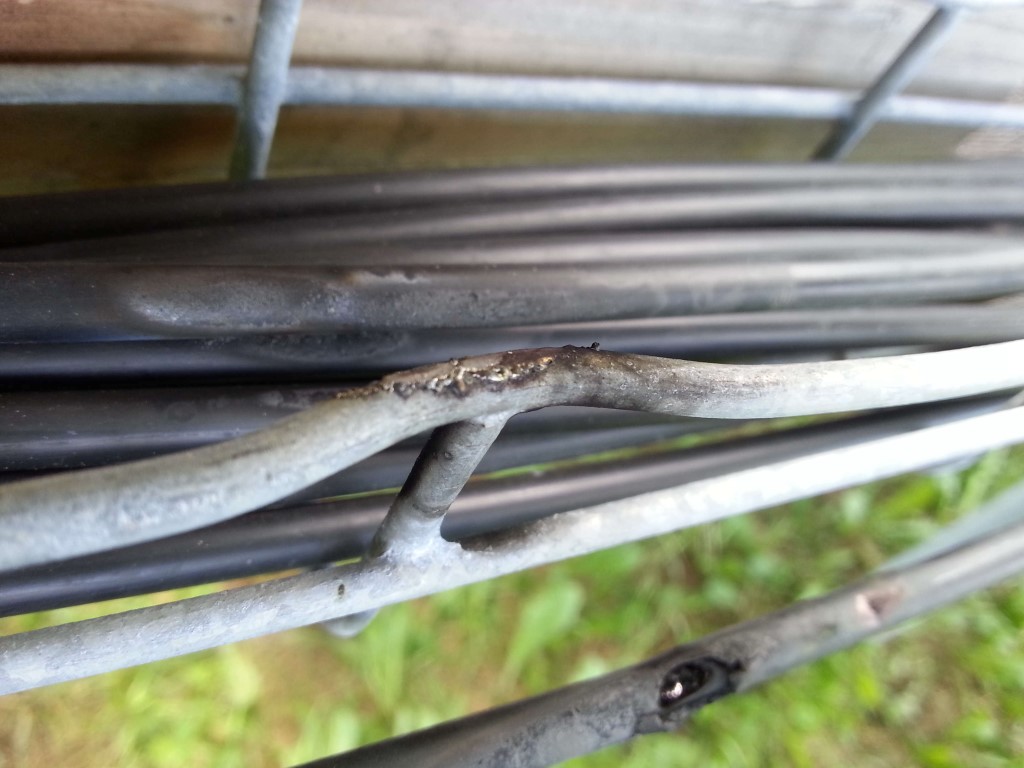
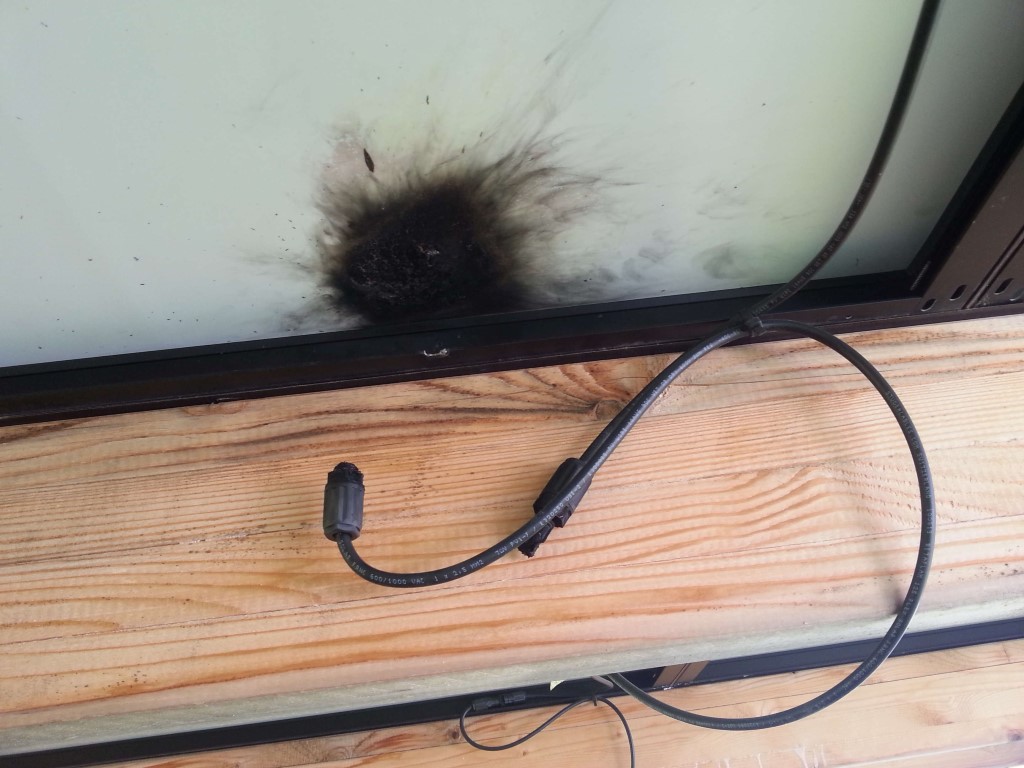
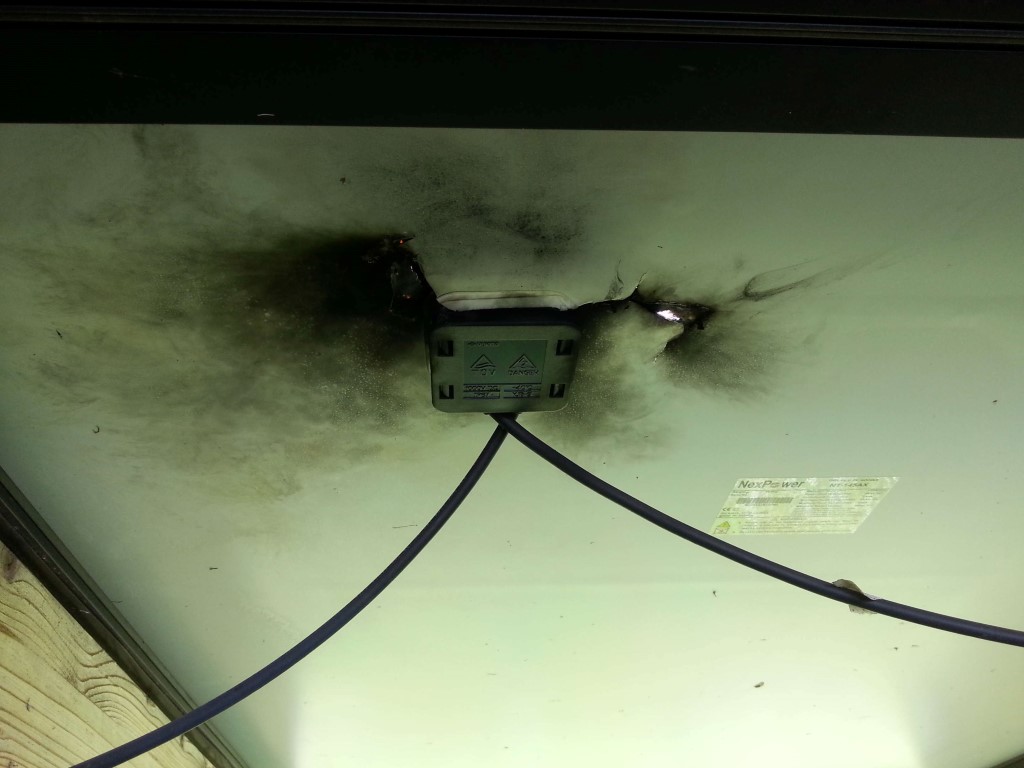
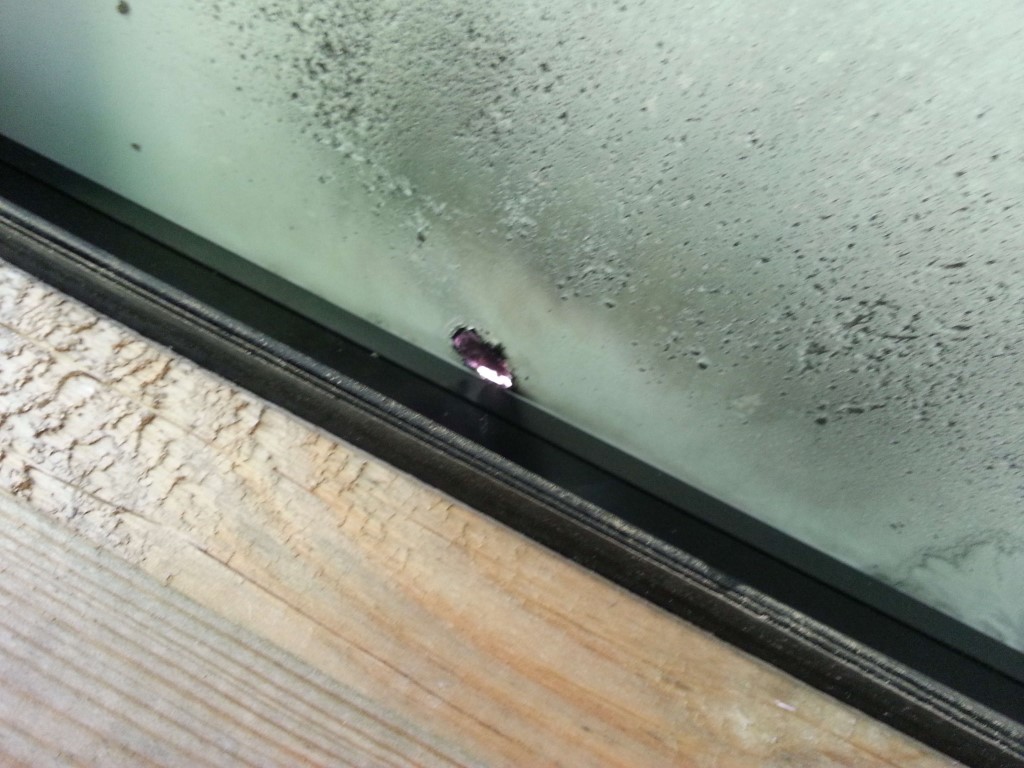




Author.
